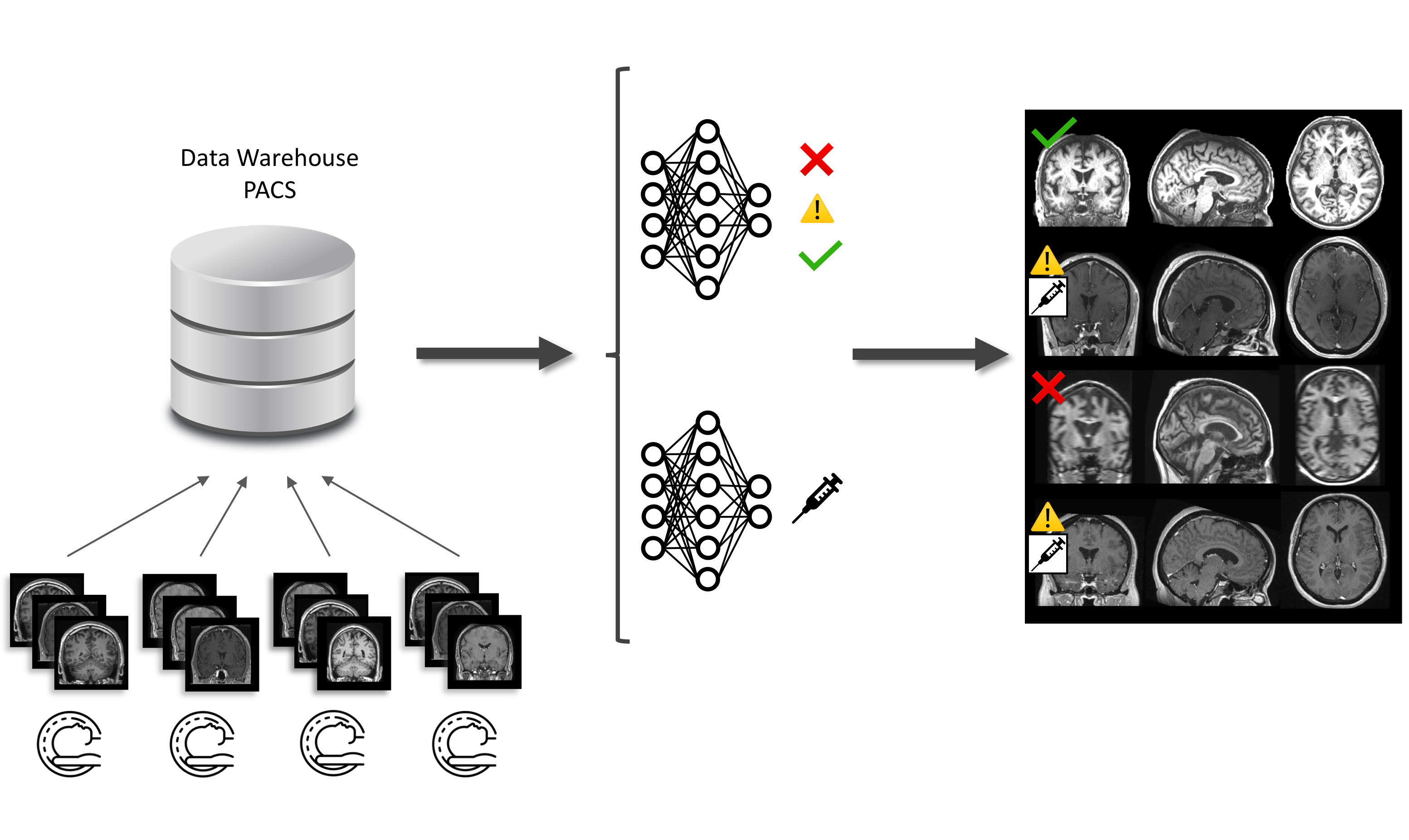
In particular, it contains over 100,000 3D T1 brain MRIs. The paper describes an AI method that performs automatic quality control of medical images, which is a prerequisite for any subsequent analyses. This has a potentially very high impact. Indeed, clinical routine data warehouses, which contain data from millions of patients, have a huge potential for training AI models. Nevertheless, the quality of imaging data is heterogeneous and thus quality control is mandatory but is not feasible manually at such a large scale. The paper was published in Medical Image Analysis, the leading journal in AI for medical imaging: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1361841521002644. It is also freely available on HAL: https://hal.inria.fr/hal-03154792v4.
This work was done as a collaboration between the ARAMIS project-team (CNRS, Inria, Inserm, Sorbonne University, Paris Brain Institute) and the EDS team of AP-HP. This work was also supported by the Abeona Foundation.